- June 2, 2025

Wheat allergy is a common health issue affecting both adults and children, directly impacting the digestive and immune systems.
With increasing awareness of this condition, it has become essential to understand its symptoms and diagnostic methods, especially with advanced tests available at precise labs like Advanced Cell Laboratories in Saudi Arabia.
 Wheat allergy is often confused with gluten intolerance, but the difference is significant:
Wheat allergy is often confused with gluten intolerance, but the difference is significant:
 Advanced Cell Laboratories is one of the leading labs in Saudi Arabia, providing precise diagnostic services including:
Advanced Cell Laboratories is one of the leading labs in Saudi Arabia, providing precise diagnostic services including:
 Wheat allergy is not as rare as some might think; it is a common disorder that requires awareness and precise diagnosis to avoid complications.
At Advanced Cell Laboratories, we provide the most accurate wheat allergy tests with detailed reports and reliable medical support.
Do not hesitate to book your appointment today for celiac testing and take advantage of advanced diagnostic packages!
Wheat allergy is not as rare as some might think; it is a common disorder that requires awareness and precise diagnosis to avoid complications.
At Advanced Cell Laboratories, we provide the most accurate wheat allergy tests with detailed reports and reliable medical support.
Do not hesitate to book your appointment today for celiac testing and take advantage of advanced diagnostic packages!
What is Wheat Allergy (Celiac Disease)?
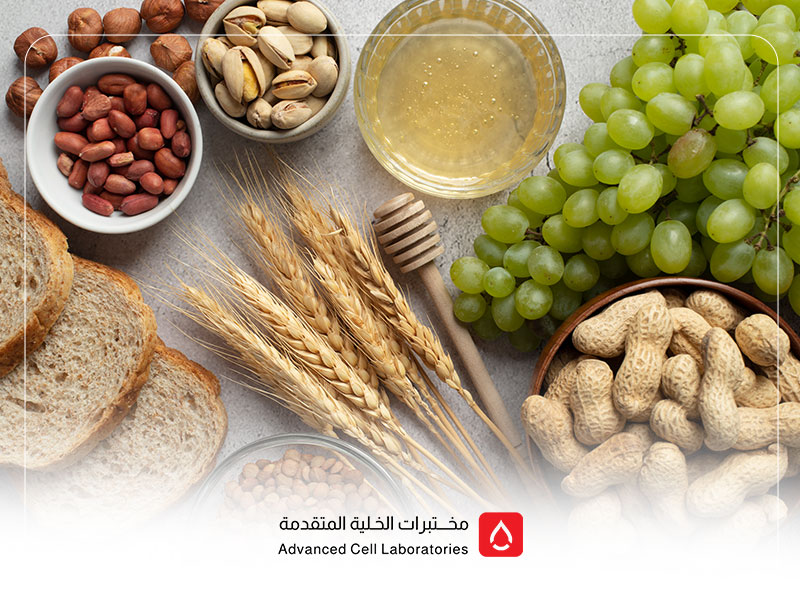
Wheat allergy or Celiac Disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder resulting from an abnormal immune response to the gluten protein found in wheat, barley, and oats. When gluten is consumed, the immune system attacks the lining of the small intestine, leading to damage and poor nutrient absorption. You can learn more about: Early detection of breast cancer (hereditary and non-hereditary) in Saudi ArabiaWhat is the difference between Wheat Allergy and Gluten Intolerance?
 Wheat allergy is often confused with gluten intolerance, but the difference is significant:
Wheat allergy is often confused with gluten intolerance, but the difference is significant:
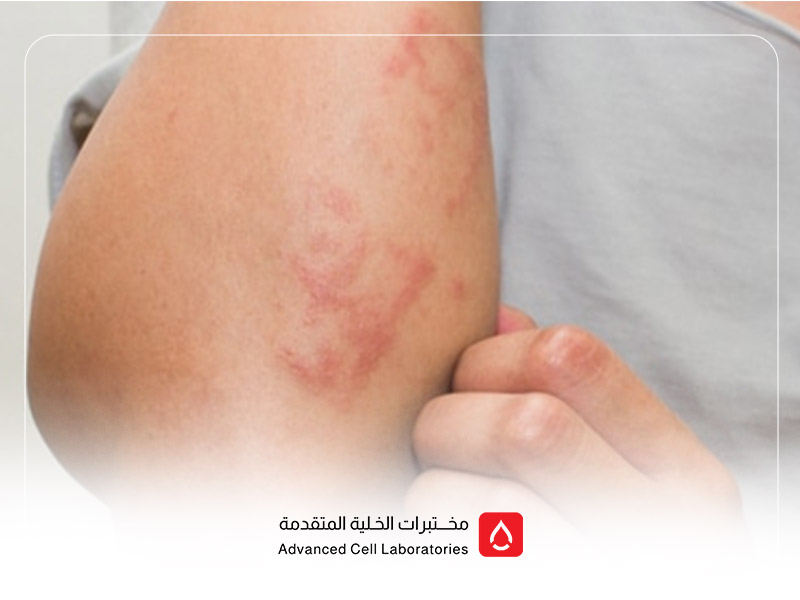
- Wheat Allergy: A severe immune response involving immediate symptoms like rash, breathing difficulties, or even anaphylaxis.
- Gluten Intolerance: A non-immune condition causing digestive symptoms like bloating and diarrhea upon gluten consumption, without a serious immune reaction.
- Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disease that damages the small intestine over time.
What are the main symptoms of Wheat Allergy?
Wheat allergy symptoms vary from person to person, including:- Abdominal pain and bloating
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Sudden weight loss
- Skin rash (especially dermatitis herpetiformis)
- Anemia
- Chronic fatigue
- Delayed growth in children
- Osteoporosis
How is Celiac Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually starts with reviewing symptoms and family history, followed by advanced tests such as:- Anti-tTG (IgA) Test: Measures anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies, the primary test for celiac disease.
- IgA and IgG Tests: To measure antibody levels related to the immune reaction to gluten.
- Genetic Gluten Test: To detect genetic mutations linked to the disease.
- Intestinal Biopsy: In some cases, to confirm small intestine damage.

Which tests should be performed?
When suspecting wheat allergy or celiac disease, it is recommended to perform:- Comprehensive wheat allergy test
- Immune test for wheat allergy
- Antibody tests (IgA, IgG)
- Other food allergy tests to identify additional potential triggers
- Asymptomatic celiac screening for at-risk or genetically predisposed family members
Can it affect children and adults?
Yes, wheat allergy can affect all age groups.- In children: May appear as chronic diarrhea, growth delays, or poor appetite.
- In adults: Manifests as diverse digestive and immune symptoms and can sometimes be silent.
Role of Advanced Cell Laboratories in Celiac Testing
 Advanced Cell Laboratories is one of the leading labs in Saudi Arabia, providing precise diagnostic services including:
Advanced Cell Laboratories is one of the leading labs in Saudi Arabia, providing precise diagnostic services including:
- High-accuracy wheat allergy testing using the latest immunoassay equipment
- Reliable and fast celiac testing in Riyadh
- Detailed reports and explanation of results for patients
- Specialized tests like anti-tTG and autoimmune analyses
Frequently Asked Questions about Wheat Allergy Testing
Should gluten be stopped before testing?
No, gluten consumption should continue to detect antibodies if present.Is celiac testing sufficient alone?
It is recommended to combine it with antibody and other immune tests for more accurate diagnosis.When is the best time for celiac testing?
When symptoms appear or there is a family history, especially in cases of hereditary gluten sensitivity.Can results be negative despite having the disease?
Yes, in some cases IgA deficiency can cause false negative results, which is why alternative tests like IgG or genetic analysis are performed. Wheat allergy is not as rare as some might think; it is a common disorder that requires awareness and precise diagnosis to avoid complications.
At Advanced Cell Laboratories, we provide the most accurate wheat allergy tests with detailed reports and reliable medical support.
Do not hesitate to book your appointment today for celiac testing and take advantage of advanced diagnostic packages!
Wheat allergy is not as rare as some might think; it is a common disorder that requires awareness and precise diagnosis to avoid complications.
At Advanced Cell Laboratories, we provide the most accurate wheat allergy tests with detailed reports and reliable medical support.
Do not hesitate to book your appointment today for celiac testing and take advantage of advanced diagnostic packages!

